
Poultry farming is an important livestock subsector. It not only provides solution for unemployment and malnutrition but also augments rural economy. This is evident from the fact that India ranks 3rd in egg production and 5th in poultry meat production. Additionally, the Indian poultry market has reached an appreciable value of INR 1,988 billion in 2020 and is predicted to grow at CARG of 15.2% in 2021-2026. The market is composed of three segments namely backyard poultry, small and marginal poultry entrepreneurs and commercial poultry players. Backyard poultry is a key component of rural household as it not only fulfills the nutritional requirement of rural households but also has the potential in adding the crucial little to the income. Commercial poultry indicates the growing market that is driven by increasing demand and supply. Tucked in between are the small and marginal poultry entrepreneurs that are crucial links in the overall supply chain of the poultry market in India. These entirely different segments co-exist and complement each other thereby making the Indian poultry market a unique sector.
India has witnessed the escalation of poultry sector from backyard farming into a techno- commercial industry due to involvement of various key players as well as an appreciable investment in breeding, hatching and rearing. This advancement in the structure and operation can be accredited to the rising eggetarian and non-vegetarian population as well as increase in the proportion of health-conscious individuals in our society. Apart from this, it is predicted that the production and consumption will increase in upcoming years due to various factors such as shift in food habits, urbanization, rise in income etc. Despite the overall growth in poultry sector one significant area that needs utmost attention for increased productivity and profit is the nutrition management of poultry. The high feed cost limits poultry productivity. In addition, limited supply and poor quality of the feed hampers optimal poultry production in our country. The reason is mainly attributable to the diverse eco-regions of the country characterized by extreme or scarce rainfall. All these factors in turn result in low protein intake by humans which poses serious health issues. Therefore, the role of feed management in poultry farming is gigantic.

CURRENT SCENARIO OF FEED RESOURCES
Success of poultry industry is primarily reflected by the quality of individual bird, managemental conditions provided to them, quality of feed provided to the birds and feed conversion efficiency of the breed employed. Of all these, quality of feed being the most expensive input deserves most crucial attention. Feed accounts for 65-70% of broiler and 75-80% of layer production cost. The most popular cereal used for poultry is maize which is used along with protein rich soybean meal. The increase in availability of maize is significantly below the production rate of meat and eggs. This necessitates the need for increasing maize and soybean production along with exploring the usefulness of alternative energy and protein rich meals in poultry diet. To meet the demand of increasing poultry industry and filling the huge gap between demand and availability of poultry feed, more scientific and holistic approach is needed. These approaches have been briefly enlisted below.
- Cereals and oil seeds which are conventional poultry feed are in direct competition with human food. With growing urbanization and decrease in agricultural land, the production of cereals and grains is not increasing at the same pace as required by the growing human population. Subsequently the availability of grains and oil seed meal is expected to decrease for the poultry industry. This escalates the cost of feed ingredients and consequently the cost of eggs and meat. This in turn may decrease the consumption of poultry products by poor section of the society impairing their protein intake. This vicious cycle goes on and on. Identification of new feed resources can solve this problem.
- Developing strains that are efficient feed convertors can also be beneficial in decreasing cost of poultry production.
- A more wholesome approach is to find for alternate and sustainable feed ingredients that are not consumed by human population and are available in plenty.
- Another strategy is utilizing technological advancements related to feed processing that allows poultry to utilize structural carbohydrates and phytate phosphates. This reduces their dependency on stored plant nutrients such as ß-glycans, pentosans, mannans, cellulose, lignin and phytic acid which not only are indigestible by poultry but also generate digestive stress to them leading to wet litter problems. Solution to this is use of feed enzymes.
- There are various technical and socioeconomic factors that constraints the use of agro industrial byproducts and· unconventional feed stuff in practical formulations despite their immense potential. These constraints can be resolved by the feed industry with the help of scientists, planners and policy makers.
- Errors in mixing feed, nutritional imbalance, inadequate storage, improper handling of raw feed ingredients and loss of potency are likely causes of nutritional deficiency disorders in poultry. This leads to poor performance of the individual birds as well as the flock without manifestation of any clinical symptoms. Therefore, such errors should be minimized in feed industry.
- Inadequate knowledge of poultry nutrition
STRATEGIES TO REDUCE FEED COST FOR ECONOMIC POULTRY FARMING
Profitability and production efficiency of poultry enterprises is increased by reduced feed costs. These targets can be achieved by scientific feeding and management strategies. These strategies are enlisted below:
- Timed feeding of broilers: Broilers are fed ad lib to allow them achieve market weight in shorter time period. However timely feeding is recommended where the birds are fed specific amount of feed 4-6 times a day and then held without feed for an hour. This is beneficial as:
- It reduces mechanical stimulation of feed intake which is routinely seen if the feeders are run throughout the day.
- During the time when birds are not provided with feed, they remain calm and quiet. This helps in better utilization of feed due to less requirement of maintenance feed.
- Amino acids and enzyme supplements: Protein is an expensive feed ingredient in feed ration and therefore is of great economic importance particularly in protein deficient tropical countries such as India. Therefore, the ration should be formulated in a way that at least optimal level of production is achieved without much expenditure on feed. The real benefit of increase in protein is usually limited to an increase of approximately 0.025% of lysine and methionine. Equivalent advantage can be gained by addition of 250g synthetic lysine and methionine per tonne of feed. Fortunately, with recent advancement in biotechnology, availability of such synthetic amino acids has become feasible which makes such an approach achievable.
Enzymes play vital role in enhancing feed utilization and reducing feed cost. For example, enzyme phytase releases some indigestible phosphorus and reduces its excretion thereby minimizing the need and cost of phosphorus supplementation. Another enzyme protease effectively releases protein anti nutrients in feed ingredients such as soybean. Also, enzymes amylase and xylanase increase the available energy by 3-5% in birds when included in the diet.
- Control of feed wastage: There are various ways through which feed is wasted without being utilized by the bird. These routes of feed wastage are burden on the economy of poultry farms and include:
i. Design of feed trough: Due to availability at low price and resistance to physical damage, elongated troughs made of galvanized metal are typically used in poultry farms. These troughs elevate the problem of feed wastage and therefore should be replaced by pan or chain feeding system.
ii. Level of feed in feeders: Feed should be adjusted and maintained at a certain level and overfeeding of the fed trough should be avoided.
iii. Beak trimming: Birds with long beaks play with the feed which leads to spillage of feed. Once the feed gets mixed with the bedding material, it is not consumed by the bird. Therefore, beak trimming is necessary not only to avoid feed spillage nut also to prevent certain vices such as cannibalism.
iv. Feed spoilage: Feeds that are not processed properly are prone to spoilage and mould growth. In addition, tropical region where the climate is hot and humid favors mould growth. To prevent this problem, 0.5% of calcium alumino silicate can be added to the feed without deteriorating the health of birds. Additionally, usage of silos can alleviate the problem of feed spoilage.
- Use of flavoring agents: Several experiments have been conducted to test the effect of feed flavors in birds. The results indicated that birds receiving flavoring agents were 8 grams heavier than the control birds at four weeks of age and 3 grams heavier at eight weeks. In addition, improvement in feed conversion was also witnessed which resulted in saving tonnes of feed.
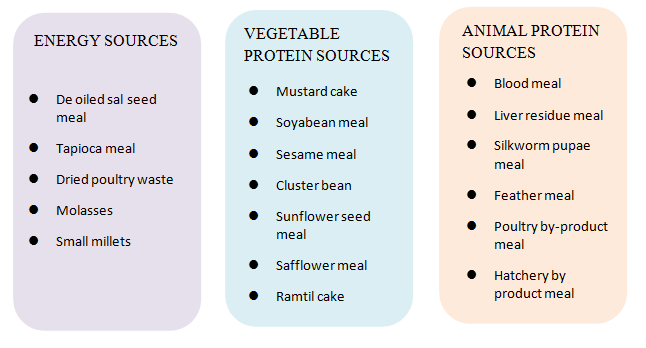
- Use of non-conventional feed: Non-conventional feed refers to feed not used traditionally for feeding purpose. There are wide varieties of NCF that have been enlisted below. They are mainly organic in nature and their economic value is less as compared to their cost of collection and transportation. Some of these feed resources may contain anti nutrients and toxic factors therefore they should be properly processed and used as supplement to overcome the limited feed resources.
CONCLUSION
Shortage of feed resources is an alarming situation in poultry industry that needs to be taken care of by efficient nutritional management. There exists a significant gap between the need and availability of feed resources that needs to be filled by various strategies such as use of non-conventional feed, flavoring agents, protein and enzyme supplements. Currently these options are not being exploited to the fullest for inclusion in poultry ration. However, with advent of knowledge and new discoveries, the future challenges will be faced to enhance the prosperous future of poultry production in India.

SAKSHI VAISHNAV, BL SAINI
Ph.D. Scholar, Division of Animal Genetics,
ICAR-IVRI, Izatnagar-243122, India
*Corresponding institutional Mail ID: sakshivaishnav1996@gmail.com









