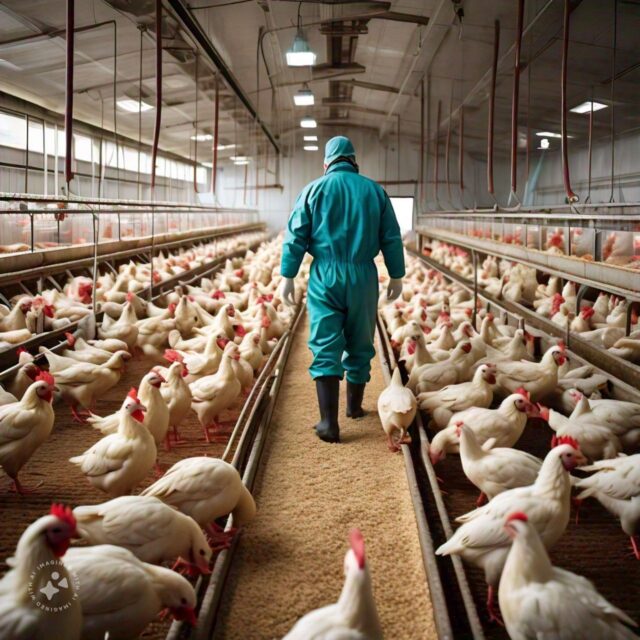
Poultry farming is a critical component of the global agricultural industry, providing a significant source of protein through meat and eggs. However, the industry faces numerous challenges, including disease outbreaks that can devastate poultry populations and pose risks to human health. Biosecurity practices are essential to mitigating these risks, ensuring the health of poultry flocks, and maintaining a safe and sustainable food supply.
Necessity of Biosecurity in Poultry Farming
Disease Prevention
One of the primary reasons biosecurity is necessary in poultry farming is disease prevention. Poultry are susceptible to a range of diseases, including avian influenza, Newcastle disease, and Salmonella. These diseases can spread rapidly within and between flocks, leading to high mortality rates and significant economic losses.
Human Health Protection
Many poultry diseases are zoonotic, meaning they can be transmitted from animals to humans. Avian influenza, for example, has caused several outbreaks in humans, sometimes with fatal outcomes. Effective biosecurity measures can reduce the risk of zoonotic disease transmission, protecting farm workers and the general public.
Economic Stability
Disease outbreaks in poultry can lead to severe economic consequences, including the loss of entire flocks, decreased production, and trade restrictions. Implementing robust biosecurity practices helps ensure the stability and profitability of poultry farms by preventing or minimizing the impact of disease outbreaks.
Environmental Protection
Disease outbreaks can also have environmental consequences, such as the disposal of infected carcasses and the use of chemical disinfectants. By preventing diseases, biosecurity measures contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the need for these practices.
Importance of Biosecurity in Poultry Farming
Maintaining Poultry Health and Welfare
Healthy poultry are more productive and have better welfare. Biosecurity measures help maintain the health and welfare of poultry by preventing diseases that cause suffering and death. This aligns with ethical standards and public expectations regarding animal welfare.
Ensuring Food Safety
Biosecurity practices are crucial for ensuring food safety. Diseases like Salmonella and Campylobacter can contaminate poultry products, posing risks to consumers. By preventing these diseases, biosecurity measures help ensure that poultry meat and eggs are safe for consumption.
Supporting Public Health
By preventing zoonotic diseases, biosecurity practices support public health. This is particularly important in areas where poultry farming is closely integrated with human communities. Effective biosecurity reduces the risk of diseases spreading from poultry to humans, protecting community health.
Facilitating Trade
Poultry products are traded globally, and countries impose strict regulations to prevent the spread of diseases through international trade. Farms with strong biosecurity practices are better positioned to meet these regulations, facilitating access to international markets and supporting the global poultry trade.
Management of Biosecurity in Poultry Farming
Effective biosecurity management involves a comprehensive approach that includes farm design, operational practices, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation. Here are key components of managing biosecurity in poultry farming:
Farm Design and Infrastructure
Site Selection
Choosing an appropriate site for poultry farming is the first step in biosecurity management. Farms should be located away from other poultry farms and areas with high wild bird populations to reduce the risk of disease transmission.
Controlled Access
Farms should have controlled access points to limit the entry of unauthorized personnel and vehicles. This includes fencing the perimeter and installing gates that can be locked.
Biosecure Buildings
Poultry houses should be designed to prevent the entry of wild birds, rodents, and other potential disease carriers. This includes using bird-proof netting, solid walls, and sealed doors and windows.
Operational Practices
Personnel Management
Farm workers are a potential source of disease introduction. Biosecurity protocols should include guidelines for personnel hygiene, such as wearing clean clothing and footwear, handwashing, and using footbaths or disinfectant mats at entry points.
Visitor Control
Visitors should be minimized, and those who must enter the farm should follow strict biosecurity procedures, including wearing protective clothing and disinfecting footwear and hands.
Equipment and Vehicle Sanitation
Equipment and vehicles that enter and leave the farm can carry pathogens. Regular cleaning and disinfection of equipment and vehicles are essential to prevent disease spread.
Feed and Water Management
Feed and water sources can be contaminated with pathogens. It is crucial to source feed from reputable suppliers, store it properly to prevent contamination, and ensure water is clean and free from pathogens.
Animal Health Management
Vaccination
Vaccination is a key component of disease prevention. Poultry should be vaccinated against common diseases according to recommended schedules.
Health Monitoring
Regular health monitoring, including visual inspections and diagnostic testing, helps detect diseases early. Sick birds should be isolated and treated promptly to prevent the spread of disease.
Quarantine Procedures
New birds introduced to the flock should be quarantined for a period to ensure they are not carrying diseases. This prevents the introduction of new pathogens to the existing flock.
Waste Management
Proper waste management is crucial for biosecurity. Manure, litter, and dead birds should be disposed of in a biosecure manner, such as composting or incineration, to prevent the spread of disease.
Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation
Biosecurity is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. Regular audits and assessments can identify weaknesses in biosecurity practices, allowing for timely improvements.
Benefits of Biosecurity in Poultry Farming
Improved Poultry Health and Productivity
Effective biosecurity practices lead to healthier poultry flocks, which are more productive. Healthy birds have better growth rates, higher egg production, and improved feed efficiency, contributing to the overall profitability of the farm.
Reduced Disease Outbreaks and Mortality
Biosecurity measures significantly reduce the incidence of disease outbreaks and associated mortality. This not only saves the lives of birds but also reduces the economic impact of disease outbreaks.
Enhanced Food Safety
By preventing diseases that can contaminate poultry products, biosecurity practices enhance food safety. This helps build consumer trust and meets regulatory standards for food safety.
Protection of Human Health
Preventing zoonotic diseases through biosecurity practices protects the health of farm workers and the general public. This is particularly important in preventing pandemics and other public health crises.
Economic Stability and Sustainability
Biosecurity contributes to the economic stability and sustainability of poultry farming. By preventing disease outbreaks, farmers can avoid the significant costs associated with disease control, lost production, and trade restrictions.
Environmental Benefits
Preventing disease outbreaks reduces the need for disposing of infected carcasses and using chemical disinfectants, contributing to environmental sustainability. Proper waste management practices also protect the environment from contamination.
Market Access and Trade
Strong biosecurity practices enable farms to meet the stringent requirements of international markets, facilitating trade and supporting the global poultry industry. This helps farmers access new markets and expand their business opportunities.
Conclusion
Biosecurity in poultry farming is a multifaceted approach that encompasses farm design, operational practices, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation. It is essential for preventing disease outbreaks, protecting human health, ensuring food safety, and maintaining economic stability. The benefits of effective biosecurity are far-reaching, contributing to improved poultry health and productivity, enhanced food safety, protection of human health, economic sustainability, and environmental protection. By prioritizing biosecurity, poultry farmers can ensure the health and welfare of their flocks, produce safe and high-quality products, and support a sustainable and thriving industry.