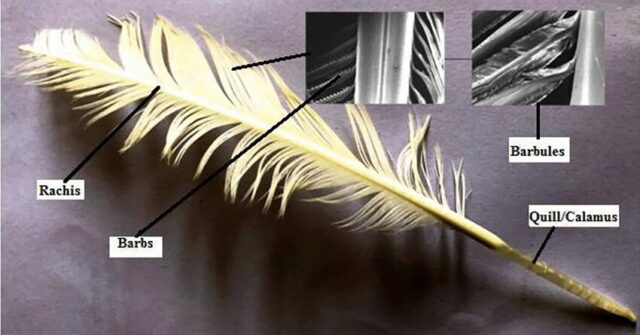
Feathers are by product of poultry, They are produced in large quantities as a by-product at poultry–processing plants, reaching millions of tons annually throughout the world, almost 40 million tones of chicken feathers produced annually across the globe have been incinerated or dumped with other waste material and are often considered a waste disposal leads to environmental pollution. However they have multiple uses viz: Automotive industries, packing material, insulation, household product, soil control, winter jackets, manufacture of Plastics, energy production, fertilizer anduberlube luxury lubricant best human hair wigs for black females college football jerseys castelli gabba asu football jersey college football jerseys air jordan 1 element yeezy shoes under 1000 college football jerseys air max 270 women jock strap inflatable kayak nike air jordan 1 elevate low custom youth nfl jersey sac à dos eastpak root substrate, livestock feed, diaper filling, aircraft, biodegradable composites, fabric etc. keeping in view of huge production and importance of feather there is need of utilization of latest technologies for commercial utilization of feather which will benefit poultry producers end user industries and protect environment.
Processing of feathers:
There are five steps involved in the processing of feather, by which the feathers are sanitized after that the feathers are separated and sorted according to their size, weight and use. These are;
De-Dusting:
It is the first system involved in processing of feathers in which dust and foreign particles are removed. The system consists of feeding equipment, pre-separator for course waste, de-dusting for elimination of fine dirt and fine particles and filtering system for bagging of waste material. Feathers are weighed up 500 lbs and are placed in the bale separator where they are broken apart and sent to loading silo from where they dropped into de-dusting machine and sent through a series of cycles to remove course waste and fine dust by vacuum chamber after this de-dusted feathers are sent to the loading silo of washing machine and the naturally bio-degradable material is bagged for land fill sites.
Washing System:
After de-dusting the feathers are ready for washing. This system consists of feeding equipment, washing chamber and centrifuge. The down and feathers are sent to the loading silo. Then up to 500 lbs are dropped into the washing which contains warm water, detergent and degreaser. These are added to ensure proper cleaning. The feathers are rinsed to remove chemicals applied in the washing and to remove fine dust and residue. In the final rinsing process sanitizing agent is added to eliminate bacteria rendering the down and feathers ensure that they will stay cleaner and fresh. These feathers are sent to centrifuge which will remove the bulk of water through whirling motion. Once this is completed the feathers are sent to the loading silo of the steam dryer.
Drying System:
This system consists feeding equipment, steam dryer, cooling chamber and the filtering system and feed into the steam dryer where the temperature is raised up to 100 c for drying and sterilizing them. After drying feathers are transferred into the cooling chamber and are kept in continuous motion through air circulation in a large cylinder where they are cooled and fluffed. The find dust is removed through filter system after washing; drying and sterilizing these feathers are sent to sorting machine.
Sorting System:
This system consists of feeding equipment sorting machine and filtering system, up to 200 lbs of feathers are sent to the loading silo where a small batches are dropped into sorting machine and are separated by swiftly circulating air into the vertical chambers, the less buoyant feathers settle into compartments according to their size and weight and down accumulate in the last compartment. This process takes four hours to fully separate down and feathers. In the sorting process the fine dust and impurities are removed through a filter system. After sorting the feathers are sent for bagging.
Bagging System:
The separate down and feathers are removed from various compartments of the sorting machine which are the transferred through a vacuum system in the large bags which are located inside each bagging chamber according to quality, use etc. They are filled, after filling the bags they are removed tied and labeled.
Uses Of Feather:
- Automotive textile: Usages of Nonwoven made out of Chicken feathers are used in seats and cushioning, Interior Linings etc.
- Packing material: while transporting delicate articles from one place to another, the cartons lined with nonwovens made out of chicken feathers are placed inside as the interlining which makes sure that the articles are tightly impact at the same place , and would be transported without any damages.
- Filter property: Nonwovens made out of chicken feathers as obvious it has a very good porosity and is lighter in weight, it has a promising future in Chemical industries as it has a good resistance to milder acids and alkalies.
- Insulation: To conduct any kind of electricity one must have a conducting element like water content (or moisture). But the chicken feathers lack such elements, so they hence a very good insulating property hence they can be act as insulating materials.
- Household product: for the Nonwovens made out of Chicken feathers are very versatile in their property they are used as decorating materials in the households.
- Soil control: The nonwovens made out of Chicken feathers are very stiff and rigid where in which when placed on the soil it will restrict the eroding of the top layered soil, thereby controlling soil erosion respectively.
- Winter jackets: The nonwovens made out of Chicken feathers are used in the jackets as the interlining where in which it keeps the body very warm.
Utilization Of Feathers:
Researchers have reported that feathers have uses in animal feeds, green house industry, erosion control, upholstery, artwork, thermal insulation, paper alternatives (49 percent wood fiber and 51 percent feather fiber), lightweight structural materials, biodegradable composites, water filtration fibers, fabric (that is biodegradable), aircraft and automotive industries and diaper filling Therefore, technologies should be developed and customized for commercial utilization of feathers for the different World (developed and developing) economies. This will benefit poultry producers, end user industries and the environment.
Manufacture of Plastics
Feathers are used in the manufacture of plastics. Plastics are of two groups, thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. Thermoplastics are manufactured from oil and natural gas. These are expensive raw materials, therefore, research has gone into finding alternative material and processes for making plastic. Thermoplastics include nylon, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and many other kinds. They are used to make consumer and industrial products ranging from toothbrush bristles to soda pop bottles to car bumpers. Thermoplastics need heat (or chemicals) to harden from a liquid into a final shape, and can be melted and remolded time and again.
Chicken-feather-based thermoplastics are stable in water while still maintaining strong mechanical properties. They are substantially stronger and more resistant to tearing than plastics made from soy protein or starch, and have good resistance to water (American Chemical Society, 2011). Feather-derived plastic can be molded just like any other plastic and has properties very similar to plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene (USDA, 2009). This makes them a unique material for packaging or any other application where high strength and biodegradability are desired.
Energy Production
In the globe, man is facing two major challenges, waste disposal and the need for an abundant source of clean energy. Feathers, a byproduct of poultry processing, usually poses a disposal challenge. The perfect solution to both of these problems is to turn the waste into energy-biofuel. This energy from garbage could cut carbon emissions by 80% while replacing the need for large amounts of petroleum. Biodiesel is a fuel comprised of mono-alkyl esters of long chain fatty acids that are derived from vegetable oils or animal fats. The main problem the biodiesel industry frequently faces is the availability of cheap and abundant, high-quality feed-stock. Thus, finding alternative, non-food, feed-stocks is a priority. Through research to produce biofuels from non-food sources, it has been discovered that feather meal offers a promising feed-stock source for biodiesel production. Poultry feathers are inexpensive and abundant. Feather meal (hydro-lyzed poultry feathers) is defined as “the product resulting from the treatment under pressure of clean, undecomposed feathers from slaughtered poultry. By boiling chicken feather meal, the 12% fat content is extracted and processed into usable biofuel.
Use as Fertilizer and Root Substrates
Feather contains about 15% protein and has high potential for use as slow release nitrogen fertilizer in greenhouses and nurseries. However, the release of nitrogen from feathers is slow to be used as a fertilizer. Plants grown in substrates containing up to 30% feather fiber were of marketable qualities. Therefore, plants can be grown in substrates containing up to 30% feather fiber, reducing reliance on peat and reducing overall cost of the substrate. Therefore, feather fiber can be used at rates up to 30% with peat and perlite substrates without negatively affecting the physical properties of the substrate. However, at 30% feather fiber with peat and bark, aggregation or clumping of the feather fiber occurs during mixing of the final substrate.
Use as Livestock Feed
Feather meal is a byproduct made of ground-up poultry feathers. It is produced by heat processing (rendering-clarify or purify by melting-heat processing) at 115° to 145° C that is sufficient to kill bacteria, viruses and many other micro-organisms. The product is an aseptic protein product that is free of potential biohazards and environmental threats. This makes feather meal safe for inclusion in animal feeds for a wide range of animal species, including fish and shrimp. Done correctly, heat processing also denatures the proteins slightly, which enhances their digestibility. Feather meal has high protein content and has a great potential as a source of protein and amino acids for animal feed. However, it has low levels of essential amino acids as well as poor digestibility. Feather meal is almost pure keratin, which is not easily degradable by common proteolytic enzymes, but can be efficiently degraded by specific proteases such as keratinase. Feather meal is hydrolyzed poultry feathers. It is rather unpalatable and should be introduced into cattle diets gradually and limited to 0.45 to 0.75 kg per head per day. In many countries, fish feeds are formulated to contain 3-7% feather meal. Crude protein in feather meal is highly digestible to fish. However, the rendering process in feather meal production is an effective method for ensuring biosecurity because processing conditions and drying denature compounds and create an unfavorable environment for viruses, bacteria and other micro-organisms to survive and grow in the product. This should assure food safety and protect human and animal health. Processing animal by-products by rendering should allow traceability of finished products for quality assurance. This can be achieved by developing HACCP programes for the feather rendering industry. Then the rendered product will be safe for compounding animal feeds.
Other Uses
Feathers fabrics have been used in erosion control. Turkey feather fiber fabrics have similar prevention of erosion. In prevention of erosion, feather fabrics increased soil moisture content and decreased soil compaction, which are critical properties for successful ecological restoration of habitats. Geese and ducks are raised in America, Asia and Europe for their feathers (Ariel, 2012). About 50 % of the down and about 42 % of the coarser feathers of geese and ducks are used to fill pillows and blankets. Feathers are also used for making feather dusters. These are cleaning devices that remove dust from objects. Goose or duck feather are used in shuttlecock. Feather are also having various ornamental uses.





Dr Nazir Ahmeda, Dr Ajaz A Darb, Dr Mir Rovidac and Dr Malik Raies Ul Islamd

a Scientist Animal Science KVK-Kupwara-SKUAST-K
b Assistant Professor Veterinary Medicine-SKUAST-K
c Guest Lecture Division of LPT-F.V.Sc. and A.H-SKUAST-K
d Scientist Animal Science KVK-Kupwara-SKUAST-K
Corresponding Author animaldr2@gmail.com









