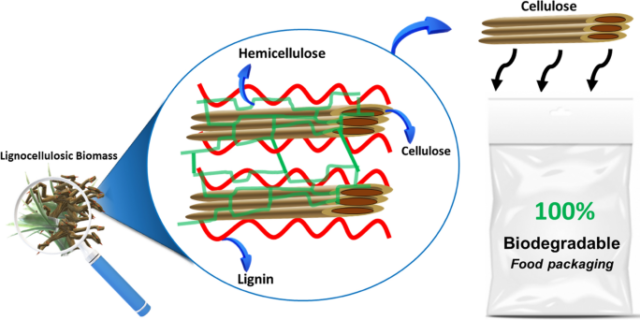
Packaging is used to protect food quality and give customer hygienic safety. It assists in the managing, conveyance, and storing of food goods by shielding them from biological, chemical, and physical harm. Additionally, it provides information about the products, such as their ingredients, features, and nutritional worth. Petroleum-based plastics have been used in the food business for many years because of their appealing qualities, which include affordability, flexibility, safety, and variety. Despite these benefits, non-biodegradability, disposal, and recycling of these materials are major drawbacks. Biopolymers, which can be obtained from marine and agricultural sources, are becoming a growing trend due to their renewable and economical nature as compared to conventional petroleum materials. The cellulose based nanocomposites are the materials which are developed from cellulose plant material and which involves isolation of nanocellulose from cellulose and reinforcement of nanocellulose in polymers. Because of cellulose’s high specific surface area and nanoscale structure, cellulosic nanocomposite has remarkable mechanical, optical, biodegradation, and barrier capabilities. Further adding cellulose nanoparticle to composite materials improves their mechanical properties; however, adding too many causes agglomeration, which results in poor mechanical performance.
Applications of cellulosic nanocomposite: –
Renewable cellulosic nanocomposite in gas/moisture barrier
Because of their use in the packaging industry, gas barrier materials are becoming more and more popular. To stop food, drink, and medication from deteriorating, these packaging materials must be impermeable to gases like oxygen, water vapor, CO2, and N2. Cellulosic nanocomposites can enhance the gas barrier properties of packing materials by limiting the entry of gases and oxygen that can degrade food quality and shelf life. Enhancements to the moisture barrier inhibit the growth of microorganisms and the absorption of moisture, which helps in maintaining the freshness of food.

Biodegradability
The discovery of substitute materials for traditional packaging polymers is crucial, as plastic pollution is a global concern. Packaging materials made of green bio-based polymers, such as nanocellulose, can be combined with other green polymers or inorganic particles, or utilized alone. Green polymers that degrade naturally, such as polylactic acid (PLA), chitosan, starch, protein, and agar, are being utilized as substitutes for conventional packaging materials.
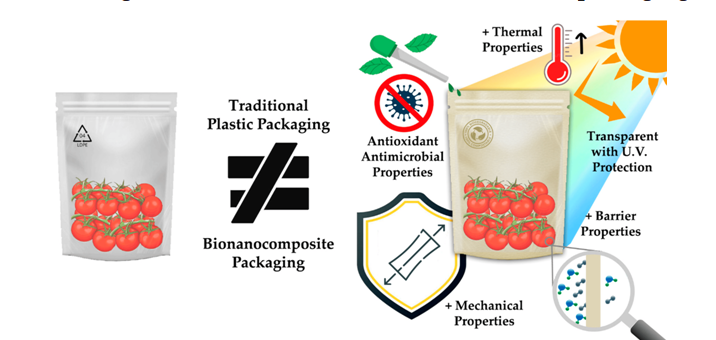
Mechanical strength
Cellulosic nanocomposites can improve the mechanical strength and stiffness of packaging materials, by providing better protection for food products during handling, transportation, and storage. The absolute qualities of a composite are mostly determined by the mechanical characteristics of the fillers. It is also well-known to be beneficial when choosing reinforcement materials. The polymer matrix of cellulose nanoparticles receives strong and high rigidity from the crystalline region.
Antimicrobial properties
Antimicrobial compounds, such as essential oils, antimicrobial peptides, or metal nanoparticles, can be injected or coated on the cellulosic nanocomposites. These substances can stop the growth of fungi, bacteria, and other microbes. The growth of fungus and bacteria on the packing material’s surface is prevented by the antibacterial compounds. This is essential for keeping food products from becoming contaminated or spoiling.
Protecting food from UV rays
UVA and UVB radiation cause more biological harm and organic compound destruction when exposed to excessive amount of sunshine. Sunburned skin, weathering, yellowing of plastics and papers, discoloration of dyes and pigments, and other issues related to UV light are all caused by UV radiation. The most prevalent natural polymer found in nature, cellulose is biocompatible, renewable, and biodegradable. The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of cellulose film is substantially lower than that of plastic substrates. Compared to many plastics, cellulose materials can withstand a significantly higher processing temperature. Cellulosic film has the high transparency and flexibility to replace plastic substrates in a variety of applications. Cellulosic nanocomposite may prevent light-induced destruction of delicate food constituents, such as flavors and vitamins, by offering UV protection.

Used in smart packaging
The creation of intelligent packaging may result from the integration of nanocomposites with sensing properties. In packaging, nano sensors are also used for the identification of food deterioration or freshness.
Conclusion
The use of renewable cellulosic nanocomposite in food packaging has created new opportunities for the production of sustainable products that could take the place of traditional synthetic materials that harm the environment. Nanocomposite materials, particularly those reinforced with cellulose, the planet’s most common biopolymer, have been emphasized as a major substitute for synthetic goods.
1Department of Renewable and Bio Energy Engineering, 2Centre of Food Science and Technology, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar (Haryana)-125004, *Corresponding Author Email:kanikapawar@gmail.com
Manik Nager1and Kanika Pawar2*