
Introduction:
Fat/Oil makes the most essential and dense source of energy in Broiler birds that may lead to higher growth in comparatively less time. Poor emulsification and lack of lipase during a young age further decrease the metabolic activity thereby creating a need of external emulsifiers in the Poultry feed that improves the utilization of Fat/Oil.
Emulsion:
An emulsion is a mixture of two products, for example, oil and water, that do not mix together i.e. immiscible. Adding an emulsifying agent (emulsifier) to the mixture causes the oil to be broken down into smaller particles that can then be dispersed throughout the water.
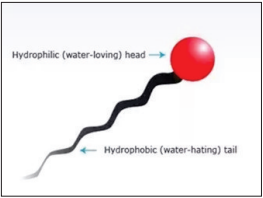
Emulsifier:
An emulsifier is a combination of hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail that acts as a surface-active agent to reduce surface tension. The hydrophilic head makes the emulsifier soluble in aqueous medium of the intestine and makes it access to a greater number of fat molecules, thereby facilitating their digestion and absorption. The emulsifiers help in improving the utilization of oil/fat, and play an important role in performing the insufficiencies of low bile production and its recirculation in young birds. The process of Emulsification or the emulsifier action depends upon the Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance (HLB) of the emulsifier.
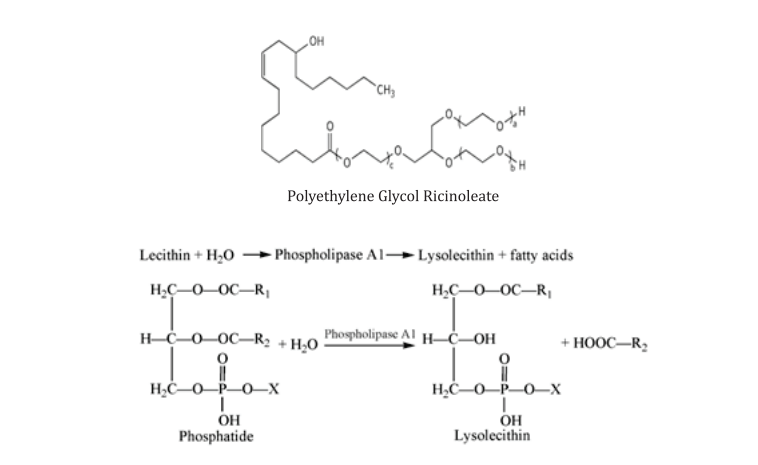
Lecithin, Lysolecithin and PEGR:
Lecithin is a widely used phospholipid extracted naturally from eggs or soybean and used in various commercially used nutritional emulsifiers in poultry feed. Soy lecithin is preferred as it is cheaper in cost and is produced as a by-product of edible oil processing from water degumming step. Lecithin is not a single phospholipid but a mixture of various Phospholipids and has very low HLB values. Partial hydrolysis converts lecithin as lysolecithin which is more hydrophilic having a higher HLB value (up to 13). Poly Ethylene Glycol Ricinoleate (PEGR) is one of the most hydrophilic surfactant/emulsifiers. PEGR is a non-ionic nutritional emulsifier that remains stable at broader pH range and even at high temperatures thereby making it suitable for pelleted feeds.PEGR, having higher HLB values(upto 18), makes it an ideal emulsifier.
HLB: Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance
The concept of HLB was proposed by Griffin in 1949 and is the best-known way to select a surfactant suitable for an application.
Definition: HLB (Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance) is an empirical expression for the relationship of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups of a surfactant.
The HLB value is used as a measure of the ratio of hydrophilic and lipophilic groups.
HLB values are calculated for non-ionic surfactants, and these surfactants have numbers ranging from 0-20.
Non-ionic surfactants don’t get dissociated when dissolved in aqueous medium and have a wide range of properties depending upon the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) ratio.
The two basic emulsion types:
1. Water-in-oil: Water is dispersed in oil
2. Oil-in-water: Oil is dispersed in aqueous phase, the most common emulsion type.
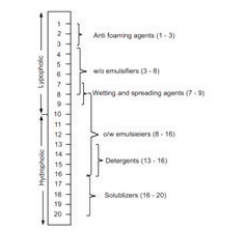
The HLB value can be used to predict the surfactant properties of a molecule:
- 1 to 3: Anti-foaming agent.
- 3 to 6: W/O (water in oil) emulsifier
- 7 to 9: Wetting and spreading agent
- 13 to 16: Detergent
- 8 to 16:0/W (oil in water) emulsifier
- 16 to 20: Solubilizer
Water-in-oil emulsions require low HLB surfactants. Oil-in-water emulsions often require higher HLB surfactants.
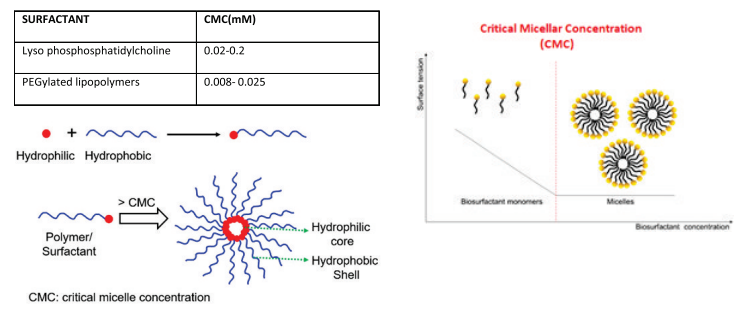
CMC: Critical Micelle Concentration
Critical Micelle Concentration is the minimum concentration of fatty acids required to form a micelle, also called as CMC. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) is a degree to measure the efficiency of a surfactant. A low CMC indicates less quantity of surfactant is required to saturate the interfaces and create micelles.
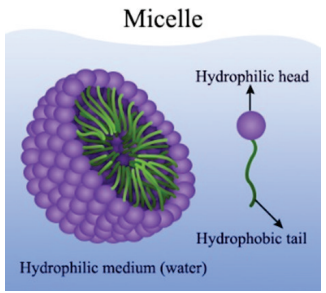
Lipid metabolism and Micelles: Stages of Lipid Metabolism in body-
- Emulsification: (Detergent action of bile salts)
- Enzymatic breakdown: (Hydrolyzed by lipase into fatty acids and mono and di-glycerides)
- Formation of micelles: (enters into cell and resynthesize triglycerides)
A micelle is an aggregated unit made up of a number of molecules of a surface-active material. Micelle formation is required for absorption of lipid contents in intestine. Monoacylglycerols, free fatty acids, phospholipids, etc are absorbed passively and to some extent actively in enterocytes of Small Intestine (duodenum and jejunum.
How CMC is responsible for better Emulsification?
When an emulsifier is added, the surface tension begins to decrease since more and more emulsifier molecules will be on the surface. As the surface becomes saturated, the addition of the emulsifier molecules will lead to micelle formation. This concentration point is called critical micelle concentration.
• At very low surfactant concentration only slight change in surface tension is detected.
• Addition of surfactant reduces the surface tension drastically.
• At CMC, surface becomes saturated and the further addition of surfactant/ emulsifier do not further reduce the surface tension.
CMC values provide a valuable guideline for comparing surfactant emulsification tendency.
Supplementation of exogenous nutritional emulsifiers has proved to be extremely helpful in metabolism of oil/fat. The efficacy of emulsifiers depends upon a number of factors e.g. the type of oil used in the formulations, HLB values, CMC, etc. The key role of nutritional emulsifiers is to enhance the digestibility of long-chain fatty acids, particularly saturated fatty acids. Emulsifiers play a crucial role in taking care of the economic aspects in poultry feed industry as emulsifiers increase the efficiency of Fat metabolism. Metabolizable Energy (ME) of the diet is an important head and emulsifiers usage has shown better results on production performance and fat/oil digestibility. The selection of an emulsifier depends on various factors two of them being HLB and CMC. The HLB value should be used as part of the selection process, as it indicates fat and water solubility in a range from zero to 20. Lower HLB surfactants are highly fat soluble, while higher HLB value surfactants are highly water soluble. When feeding poultry, a higher number would be desirable because the environment of the gut is mostly aqueous. Lower CMC values indicate that a very low quantity of emulsifiers will lead to micelle formation thereby improving better fat metabolism in the bird’s body.
An ideal oil-in-water emulsifier will possess high HLB value, low CMC value thereby leading to best emulsification and as a result better health and improved economic return (Rol) can be realised by the farmers/feed millers.
For more information, contact: srijit.tripathi@vetline.in
Also, read | Impact of Climate Change on Livestock
Author:
Dr. Srijit Tripathi, Global Technical Manager, Vetline
















