Introduction
There are many problems arise while manufacturing of major dairy products among which one major is of the utilization of dairy by-products. Due to the unique nutritional value its proper utilization have major role through most profitable ways. Especially in developing countries where the shortage of milk is more so conversion of it into the most nutritious food is paramount importance. It is realized economic disposal of by-products is one of prerequisites of profitable dairying.
Definition
‘A Dairy by-product may be defined as a product of commercial value produced during the manufacturer of a main product.’
Classification
(A) By-products of the Western dairy industry-
Main product By-product
Cream – Skim milk
Butter – Butter milk
Cheese, Casein – Whey
(B) By-products of Indian dairy industry-
Main product By-Product
Ghee – Lassi (Ghee residue)
Chhana/Paneer,
Cheese, Casein – Whey
Cream – Skim milk
Butter – Butter milk
Methods of Utilization
The utilization of the various by-products resulting from the manufacture of different products.
(1) Skim milk
Skim milk is made when all the milk fat removed from whole milk.
Composition of skim milk – water- 90.6%, Fat – 0.1%, SNF – 8.7%, protein- 3.6%, Lactose – 5.0%, Ash- 0.7%. It’s use in the standardization of milk, cream etc.
A) Flavoured milk
Flavoured milk are milk to which some flavours have been added.
Flavoured milk fat level is lower than 1-2%.
B) Cultured buttermilk – This is obtained by inoculation and incubation of pasteurized skim milk with lactic starter.
C) Acidophilus milk – Acidophilus milk is a probiotic drink; this type of fermented milk is produced by development in milk or culture of Lactobacillus acidophilus.
Acidophilus milk has therapeutic and health-promoting properties.
D) Condensed skim milk
Condensed milk are the product obtained by evaporating part of the water of whole milk or fully or partly skimmed milk, with or without the addition of sugar.
According to PFA rules (1976) the various condensed skim milks have been specified-
Unsweetened condensed skim milk (evaporated skimmed milk) – contain 20.0% total milk solids and 0.5% Fat.
Sweetened total milk solid and 0.5% Fat and 40.0% cane sugar. Condensed skim milk – contain 26.0%.
E) Skim milk Cheese
Cheese is the milk product obtained by draining after the coagulation of milk with a harmless milk-coagulating agent, under the influence of harmless bacterial culture. It contained 43.0% moisture and 42.0% milk fat.
Some examples of cheese made from skim milk – Cottage cheese, Baker’s cheese, Gammelost cheese, Sapsago cheese etc.
F) Casein
Casein is the most important protein component in milk, both quantitatively and nutritionally. Found in form of a calcium caseinate-phosphate complex. It forms more than 8% of the total protein in milk.
Important utilization of skim milk is in the production of industrial casein (non-food item).
There are two types of industrial casein – Acid casein and rennet casein.
Acid casein – It has, faint pleasant odour, slightly acidic taste, pH about 5.2 and 10.0% moisture, fat – 1%.
Uses of acid casein – Leather finish, textile finish, spreader of insecticide etc.
Rennet casein – It has a faint agreeable odour, tasteless, pH about 7.0 and moisture 10.0%.
Uses of rennet casein – Plastics such as buttons, costume jewellery and umbrella handle etc.
Method of manufacture of casein

Edible Casein
Edible casein may be defined as casein which has been isolated from skim milk by taking special precautions to ensure its suitability for use in patented food and pharmaceutical preparations.
Special precautions taken should be –
i) Precipitation of the curd at pH 4.1-4.3.
ii) At least 3 separate washing of the curd in waters of proper pH, with contact time 15-20 min.
iii) One washing with hot water at 71- 77°C (160-170°F), which effects the pasteurization of curd for reducing bacterial count.
iv) Last washing with neutral water at 41°C (105°F).
Edible casein is used in various food products like- ice cream, coffee whiteners, whipping powders etc.
(2) Buttermilk
Buttermilk is the slightly sour liquid left after butter has been churned, used in baking or consumed as a drink. Composition of buttermilk – water -91.0%, Fat – 0.4%, protein – 3.4%.
It can be utilized in the preparation of-
A) Condensed buttermilk – also known as semi-solid buttermilk. 5-6% acidity is necessary for long-keeping quality.
B) Dried buttermilk
C) Soft cheese from buttermilk etc.
(3) Whey
The whey obtained as a by-product of cheese industries has long since been employed in the production of fermented beverages, both alcoholic and Non-alcoholic (acidic).
i) Utilization of whey in the production of a soft drink called whevit.
ii) Yeast-whey – This is a newly developed product. food supplement rich in proteins and vitamins.
iii) Whey paste – Pre-concentrating a mixture of whey and skim milk in a vacuum evaporator, and adding sugar syrup, butter and cream so as to obtain 15% sugar, 15%fat, 65%total solids in products.
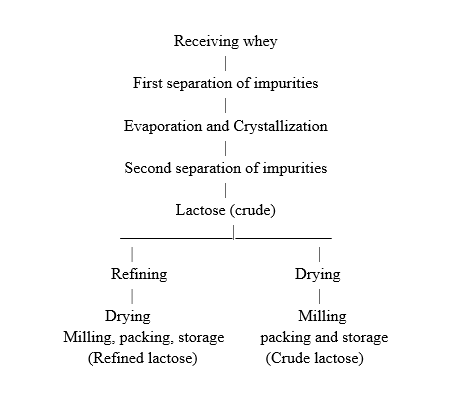
iv) Lactose
lactose or milk sugar is true solution in the milk serum. It is one-sixth as sweet as sucrose.
Lactose is responsible, under certain conditions, for the defect known as “sandiness ” in ice cream and sweeten condensed milk.
Uses –
(i) In the preparation of humanized milk
(ii) In infant food
(iii) In solid pharmaceutical preparations such as pills and tablets.
Method of manufacture
(4) Lassi
It also called chhas or matha, refers to Desi buttermilk, which is By-product obtained when churning curdled whole milk with crude indigenous devices for the production of desi butter (makkhan).
It is largely consumed by the producer’s household after seasoning it with salt or sugar.
Composition of Lassi – water – 96.2%, Fat – 0.8%, Solid-not-fat – 3.0%, protein – 1.4%, Lactose – 1.2%, Ash – 0.4%.
(5) Ghee-residue
It is also known as sweet cream butter.
This is a nutritious food containing fat (61.4%), water – 9.7%, desaturated protein, burnt lactose and minerals.
It can be utilized in the preparation of candy and chocolate.
Authors:
Bhagwati Ninama, Pranav Chauhan and Narendra Kumar Nayak
Department of Livestock Product Technology, College of Veterinary Science and Animal
Husbandry, (NDVSU), Mhow, Indore (MP) 453446, India